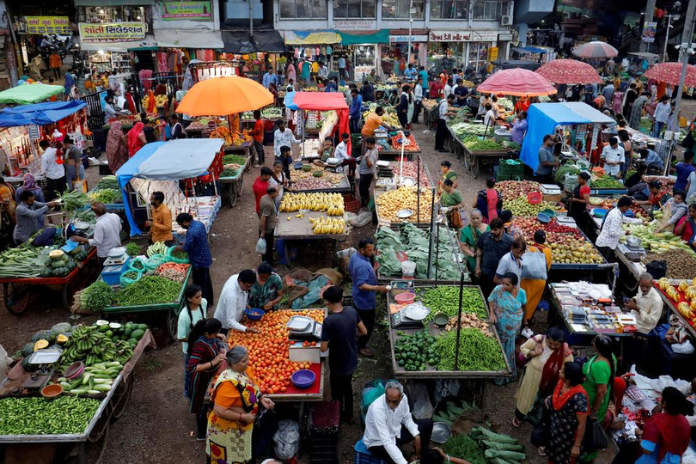
India’s retail inflation, measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), fell to 3.61% in February 2025, marking a seven-month low. This decline, which beat market expectations, was primarily driven by a significant drop in food prices.
A major reason for the fall in inflation is the reduction in Consumer Food Price Inflation (CFPI), which dropped to 3.75% in February from 5.97% in January. Lower prices of vegetables, eggs, meat, fish, pulses, and dairy products contributed significantly to this downward trend.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) aims to keep inflation around 4% with a margin of ±2%. With inflation now below this target, the central bank may consider another interest rate cut in its upcoming monetary policy meeting on April 9. Last month, the RBI had already reduced the repo rate by 25 basis points due to easing inflation concerns.
While inflation is easing, India’s industrial output is gaining momentum. The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) grew by 5% year-on-year in January 2025, supported by the manufacturing and mining sectors. This indicates strong economic activity, which could further influence RBI’s decision-making.
With inflation under control and industrial growth improving, India’s economic outlook appears stable. If food prices remain low and economic indicators stay positive, consumers can expect a more favorable cost of living, and businesses may benefit from reduced borrowing costs.
The RBI’s upcoming policy decision will be closely watched as it weighs inflation trends and economic growth to decide the next move on interest rates.
(with agency inputs)